Create a twitch clone using React — 6
by Nabendu Biswas / May 17th, 2019
#javascript #react #webdev
Series: Twitch-react
Welcome to Part-6 of the series. Let’s start where we left. We will next create our Delete component. We are going to show a modal to the delete the stream.
We will be using a React Portal for this, as creating a Modal is tricky in React.
So, go ahead and create a Modal.js file inside the components folder. Add the following code to it. We are using the method createPortal, in which the second argument is to select an id modal.
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import history from '../history';
import './Modal.css';
const Modal = props => {
return ReactDOM.createPortal(
<div onClick={() => history.push('/')} className="modal-body">
<div onClick={(e) => e.stopPropagation()} className="modal-main delete-modal">
<div className="header">Delete Stream</div>
<div className="modal-text">Are you sure you want to delete this Stream?</div>
<div className="modal-buttons">
<button className="deleteBtn">Delete</button>
<button className="editBtn">Cancel</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>,
document.querySelector('#modal')
);
};
export default Modal;
Let’s create the id=”modal” inside our index.html file in public folder. As, most of you might know that the whole React application is rendered in id=”root”. So, with the help of React Portal, we can create another element and use it to show our modal.
…
…
<div id="root"></div>
<div id="modal"></div>
…
…
Next, create Modal.css file inside the components folder. Add the code to show a basic modal.
.modal-body {
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
width:100%;
height: 100%;
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.6);
}
.modal-main {
position:fixed;
background: white;
width: 25%;
height: auto;
top:50%;
left:50%;
transform: translate(-50%,-50%);
}
.delete-modal{
display: grid;
grid-gap: 10px;
border: 1px solid #c1c1c1;
}
.modal-buttons{
justify-self: end
}
Now, go ahead and add this Modal component in our StreamDelete.js file.
import React from 'react';
import Modal from '../Modal';
const StreamDelete = () => {
return (
<div>
StreamDelete
<Modal />
</div>
)
}
export default StreamDelete;
Now, head over to http://localhost:3000/streams/delete in browser and you can see our modal.
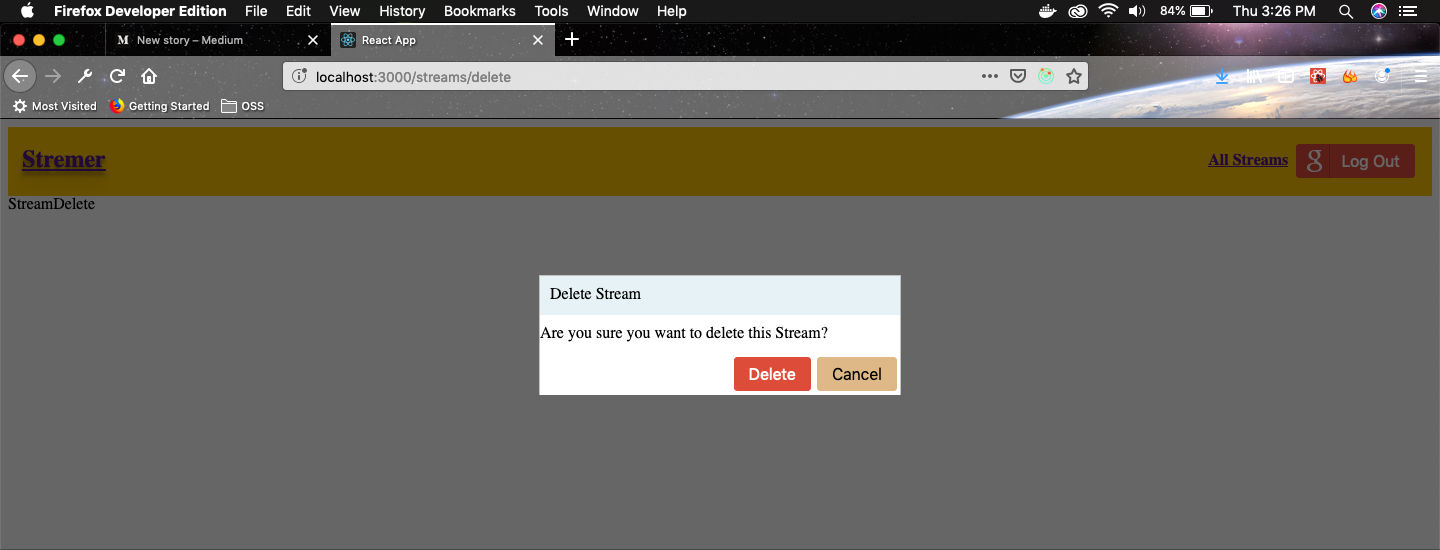 Beautiful Modal
Beautiful Modal
One thing to notice in Modal.js file is that, we have used an onClick event handler on the main div. It is used to navigate the user to the home page from, if he clicks anywhere outside the modal window ie the grey area.
But not to do so, if he clicks anywhere inside the modal window, we have use e.stopPropagation.
<div onClick={() => history.push('/')} className="modal-body">
<div onClick={(e) => e.stopPropagation()} className="modal-main delete-modal">
...
</div>
...
</div>
Our Modal Component is not reusable, so let’s make it more reusable so that we can use in some other place also. We will move all the hard-coded logic into the parent component and use it via props here. So, in Modal.js make the following changes.
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import './Modal.css';
const Modal = props => {
return ReactDOM.createPortal(
<div onClick={props.onDismiss} className="modal-body">
<div onClick={(e) => e.stopPropagation()} className="modal-main delete-modal">
<div className="header">{props.title}</div>
<div className="modal-text">{props.content}</div>
{props.actions}
</div>
</div>,
document.querySelector('#modal')
);
};
export default Modal;
Next, in StreamDelete.js, add those parts.
import React from 'react';
import Modal from '../Modal';
import history from '../../history';
const StreamDelete = () => {
const actions = (
<div className="modal-buttons">
<button className="deleteBtn">Delete</button>
<button className="editBtn">Cancel</button>
</div>
);
return (
<div>
StreamDelete
<Modal
title="Delete Stream"
content="Are you sure you want to delete this Stream?"
actions={actions}
onDismiss={() => history.push('/')}
/>
</div>
)
}
export default StreamDelete;
Now, we will add logic to those Delete and Cancel buttons. So, move to App.js and change the delete to include id also.
const App = () => {
return (
<div>
<Router history={history}>
<div>
<Header />
<Route path="/" exact component={StreamList} />
<Route path="/streams/create" exact component={StreamCreate} />
<Route path="/streams/edit/:id" exact component={StreamEdit} />
<Route path="/streams/delete/:id" exact component={StreamDelete} />
<Route path="/streams/show" exact component={StreamShow} />
</div>
</Router>
</div>
);
}
Next, goto StreamList.js and add logic to the delete button there.
renderAdmin(stream) {
if(stream.userId === this.props.currUserId) {
return (
<div>
<Link to={`/streams/edit/${stream.id}`} className="editBtn linkBtn">Edit</Link>
<Link to={`/streams/delete/${stream.id}`} className="deleteBtn linkBtn">Delete</Link>
</div>
)
}
}
Now, if you go to homepage and click on Delete button, it will open our modal.
Next, we will change our StreamDelete.js to a class based component as we will use redux state here.
import React from 'react';
import Modal from '../Modal';
import history from '../../history';
class StreamDelete extends React.Component {
renderActions() {
return (
<div className="modal-buttons">
<button className="deleteBtn">Delete</button>
<button className="editBtn">Cancel</button>
</div>
);
}
render() {
return (
<div>
StreamDelete
<Modal
title="Delete Stream"
content="Are you sure you want to delete this Stream?"
actions={this.renderActions()}
onDismiss={() => history.push('/')}
/>
</div>
)
}
}
export default StreamDelete;
Now, we will use all redux state in our StreamDelete component. The logic will be almost similar to what we did for StreamEdit component. So, go ahead and edit the StreamDelete.js
import React from 'react';
import Modal from '../Modal';
import { connect } from 'react-redux';
import { fetchStream, deleteStream } from '../../actions';
import history from '../../history';
class StreamDelete extends React.Component {
componentDidMount() {
this.props.fetchStream(this.props.match.params.id);
}
renderActions() {
const id = this.props.match.params.id;
return (
<div className="modal-buttons">
<button onClick={() => this.props.deleteStream(id)} className="deleteBtn">Delete</button>
<button onClick={() => history.push('/')} to={'/'} className="editBtn">Cancel</button>
</div>
);
}
renderContent() {
if(!this.props.stream) {
return 'Are you sure you want to delete this Stream?'
}
return `Are you sure you want to delete the Stream - ${this.props.stream.title}`
}
render() {
return (
<Modal
title="Delete Stream"
content={this.renderContent()}
actions={this.renderActions()}
onDismiss={() => history.push('/')}
/>
)
}
}
const mapStateToProps = (state, ownProps) => {
return { stream: state.streams[ownProps.match.params.id] }
}
export default connect(mapStateToProps, { fetchStream, deleteStream } )(StreamDelete);
One last thing is to update deleteStream() inside index.js in action folder. We added history.push(‘/’) similar to edit and create to move the user back to the homepage once a stream is deleted.
export const deleteStream = (id) => async dispatch => {
await streams.delete(`/streams/${id}`);
dispatch({ type: DELETE_STREAM, payload: id });
history.push('/');
}
So, go ahead and delete a stream. Everything should work properly.
This concludes part-6 of the series. You can find code till this point here.