JavaScript Crash Course for Beginners -4
by Nabendu Biswas / August 28th, 2020
#javascript #beginners #webdev
Series: JS-Basics
Welcome to part-4 of the series.
Conditionals
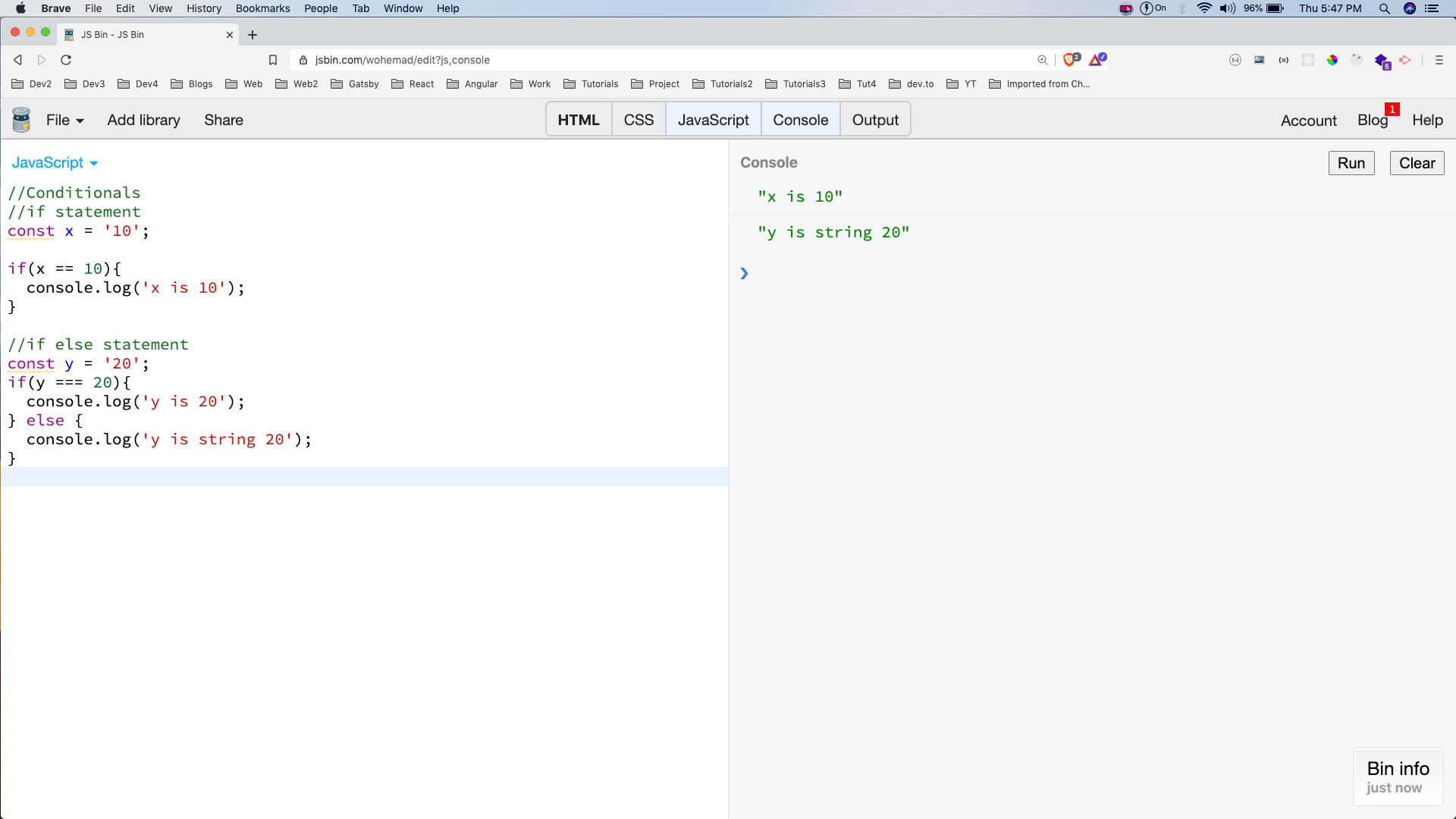
The first conditional which we are going to check is the if statement. The statement within the curly brackets will execute only if the condition is true.
We compare two things in JavaScript with the == operator.
const x = '10';
if(x == 10){
console.log('x is 10');
}
So, here the console.log statement will be printed. But there is a problem in the above statement because x is string 10 and we are comparing it with numeric 10. Both are becoming equal because JavaScript changes the type of string to number before comparing.
We can solve this by using === operator, which does strict comparison and doesn’t changes the type of operands.
The below statement also shows a if-else statement, in which the else part will run when the if part is false.
const y = '20';
if(y === 20){
console.log('y is 20');
} else {
console.log('y is string 20');
}
We can see both above statements in action in the below jsbin.
 if and if-else
if and if-else
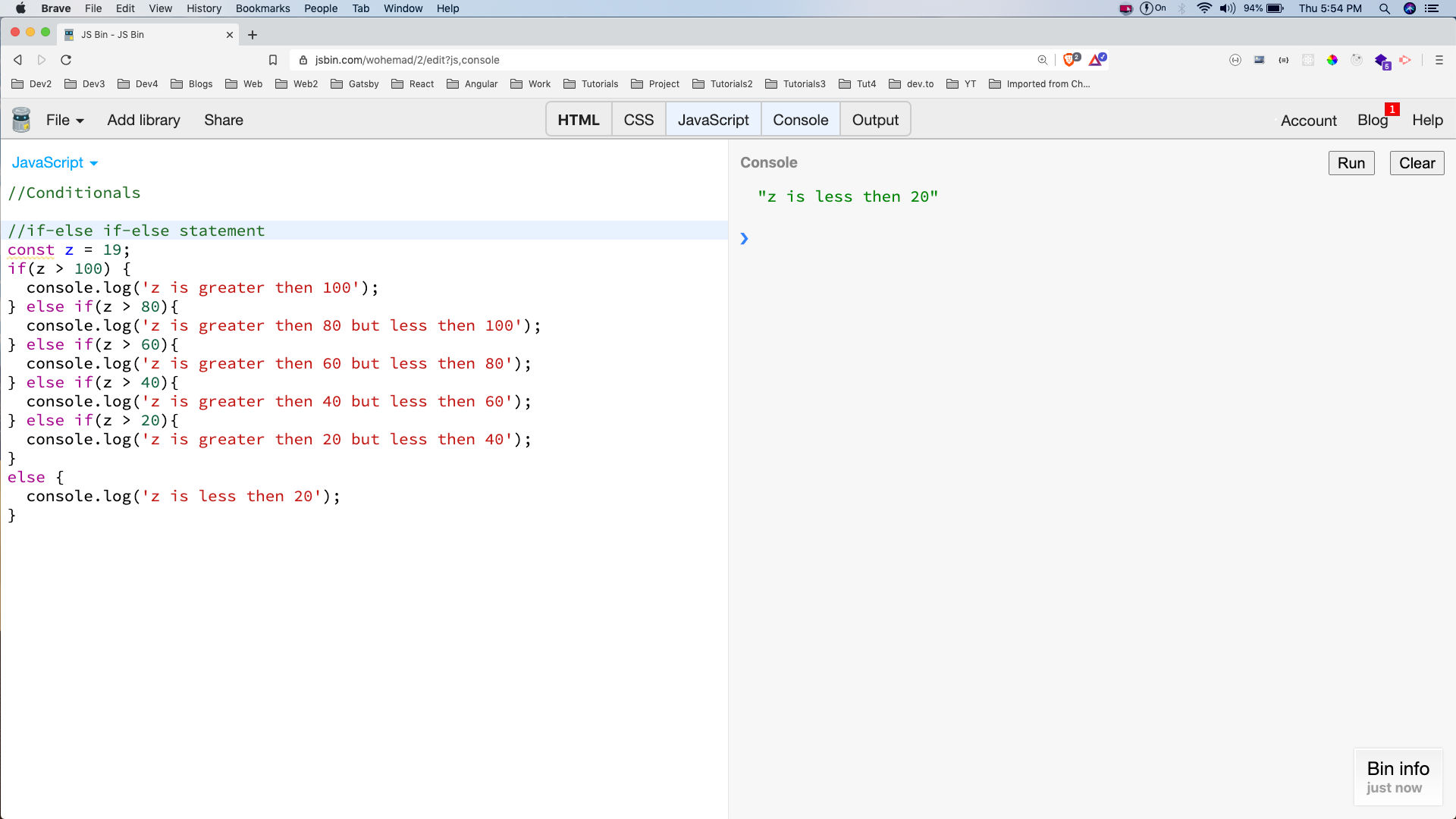
We can also have a chain of else if statements called if-else if-else statements. Suppose, we need to check more than 2 conditions, then these types of statements are required.
Now, we have a chain of else if statements. The compiler move through each statements and check whether it is true, if it is not true it will move forward.
In our case none of the statements are true so the else statement will execute.
 if-else if-else statements
if-else if-else statements
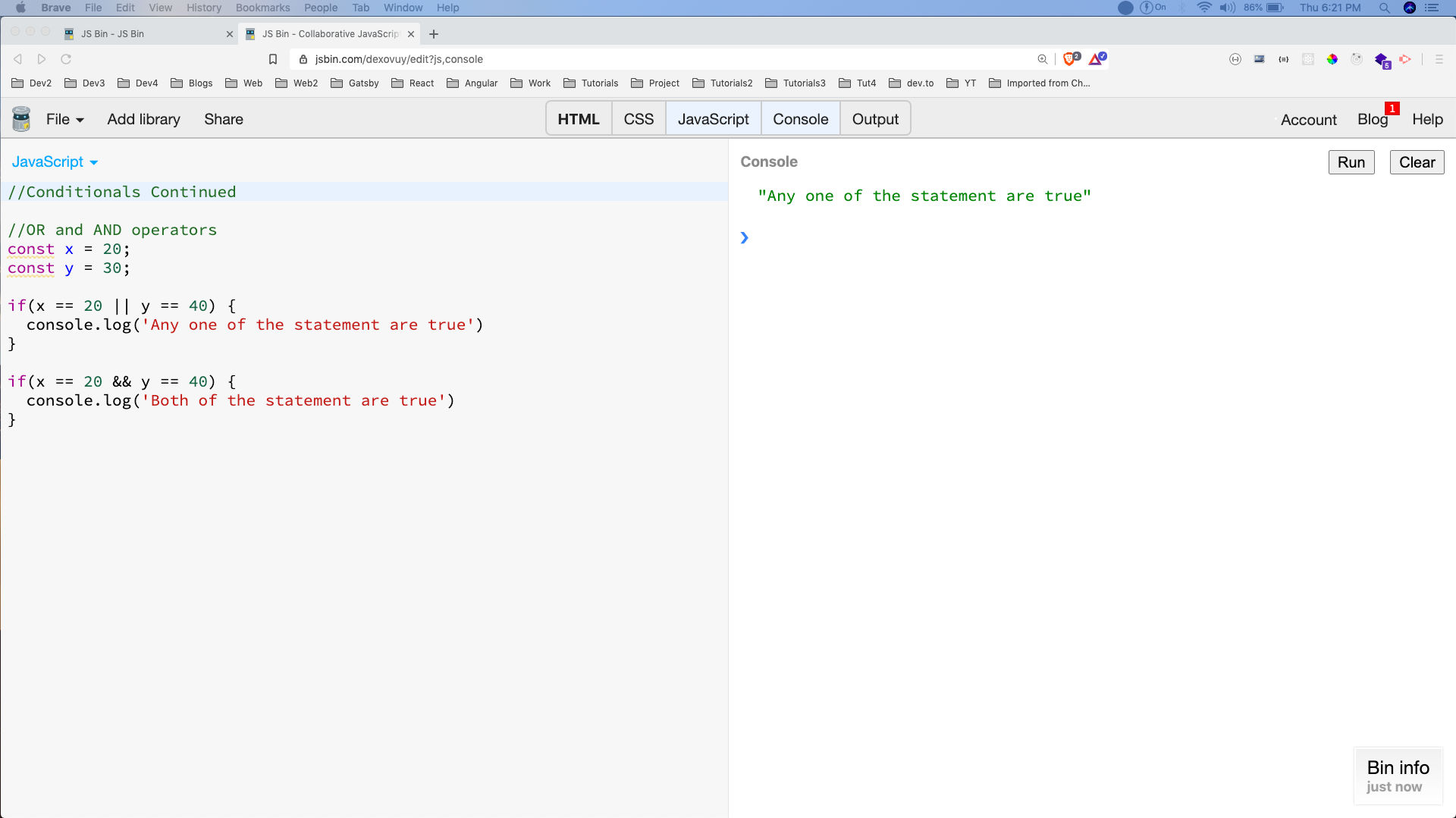
One more important concept before we move forward is the OR and AND operators. Both of these are mainly used inside a conditional statement.
As the name suggest the OR operator will return true if any of the condition is true. The AND operator will return true only if both conditions are true.
 OR and AND operators
OR and AND operators
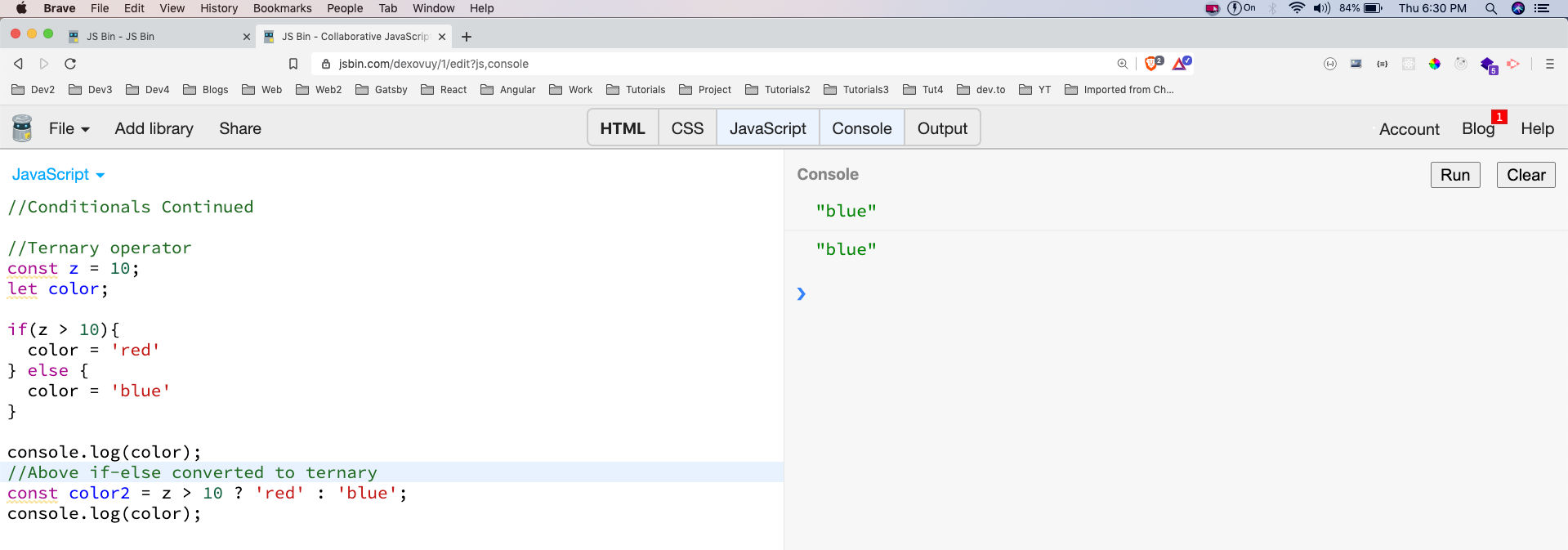
Instead of using a normal if else statement we can use the Ternary operator. Below is an example for the same, where we convert a normal if-else statement to ternary operator.
 Ternary operator
Ternary operator
We also have another statement called Switch statements. It can be used as a replacement for if-else if-else statements.
 switch statement
switch statement
Functions
As with any other language, function is building block of JavaScript. They are used to organise code in smaller manageable parts.
Below are four common ways to use function in JavaScript. The first two are the old way in which we have a function keyword. First one is called function declaration and the second one is function expressions, where we are assigning a variable to function.
The third and the fourth way are for arrow function. In the fourth way, we are using a condensed way of arrow function. It can be used when we have just one statement and it’s a return.
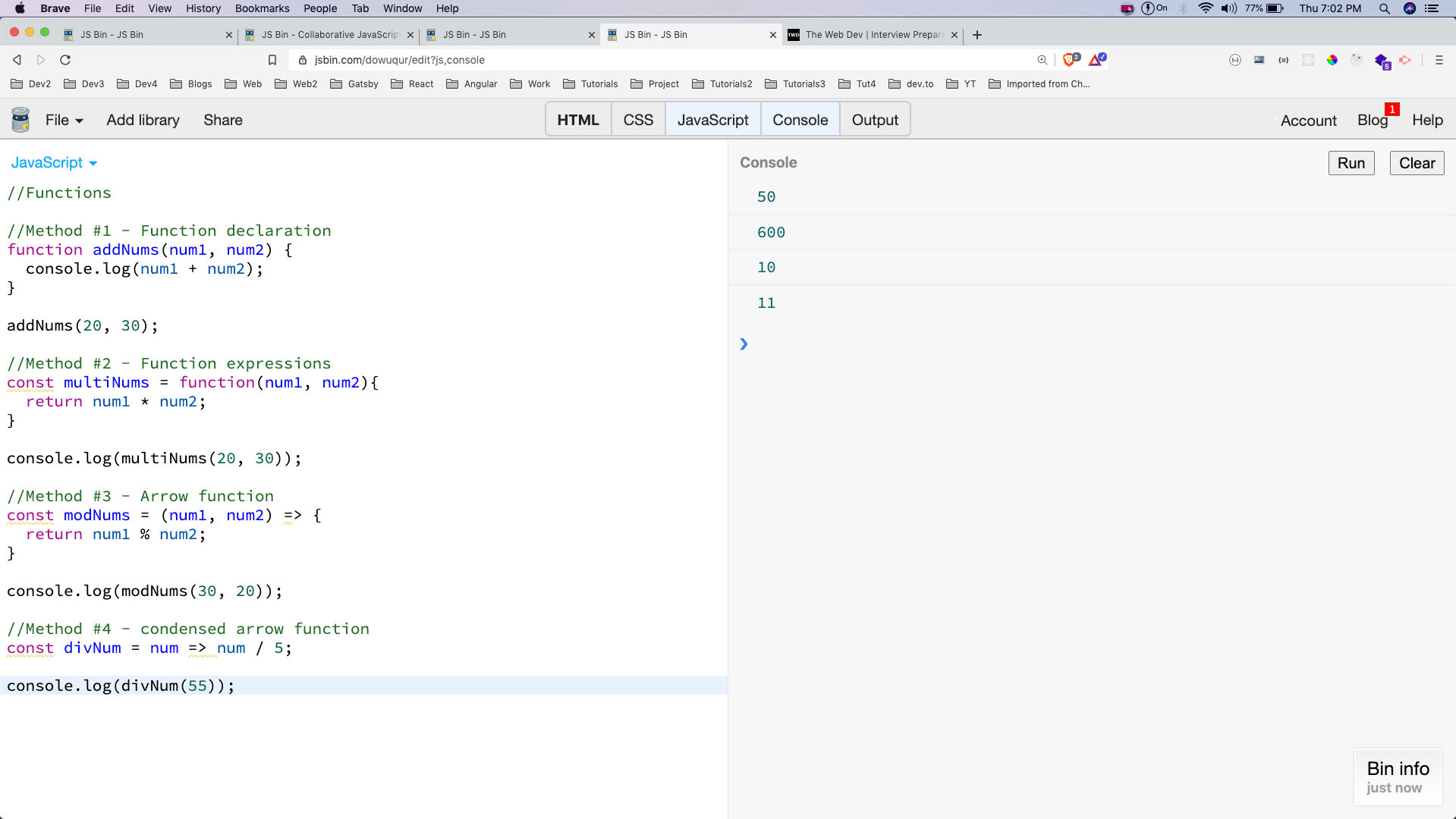 Functions
Functions
This completes our JavaScript Crash course.
You can find the jsbins used in this part below.
https://jsbin.com/wohemad/3/edit?js,console
https://jsbin.com/dexovuy/3/edit?js,console