ReactJS Tutorial for Beginners -17
by Nabendu Biswas / October 27th, 2020
#javascript #beginners #react
Series: React-Basics
Welcome to part-17 of the series. We will learn about Context in this part.
Context
Context provides a way to pass data through the component tree, without having to pass props down manually at every level.
We have a problem, when we need a prop some level deep from the parent. We need to pass the prop through all the nested component.
In the below example the Username prop of the App Componet is required by Component C. Now, it have to pass through the Component A and B also. Although they don’t need it.
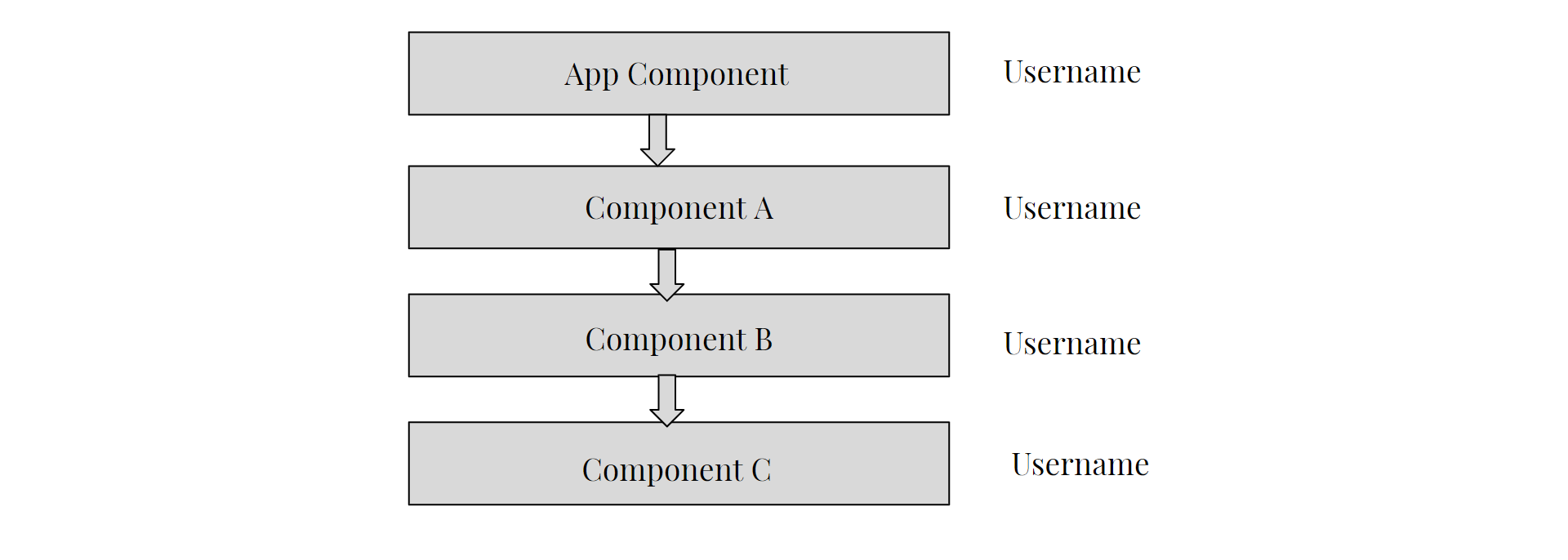 The problem
The problem
Now, we will understand this with an example. Create a file Child.js inside components folder and put simple text in it as below.
 Child.js
Child.js
Next, create a file Parent.js inside components folder and call the Child component from it, as below.
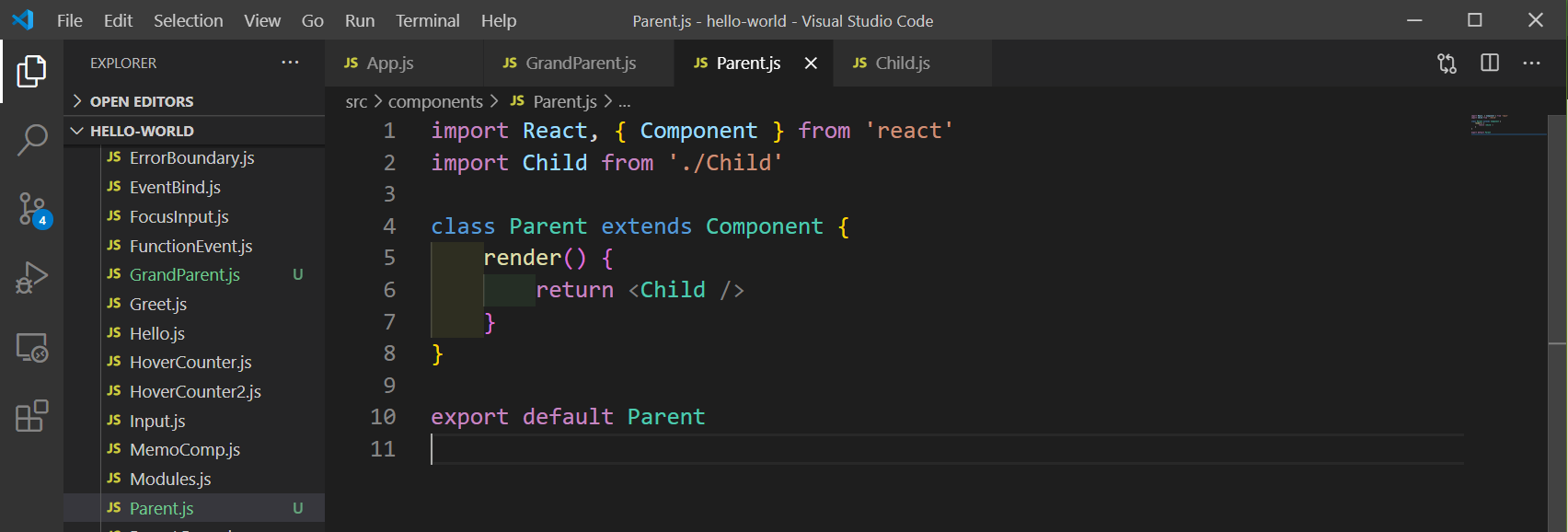 Parent.js
Parent.js
Then create a file GrandParent.js inside components folder and call the Parent component from it, as below.
 GrandParent.js
GrandParent.js
Now, render it from the App.js file.
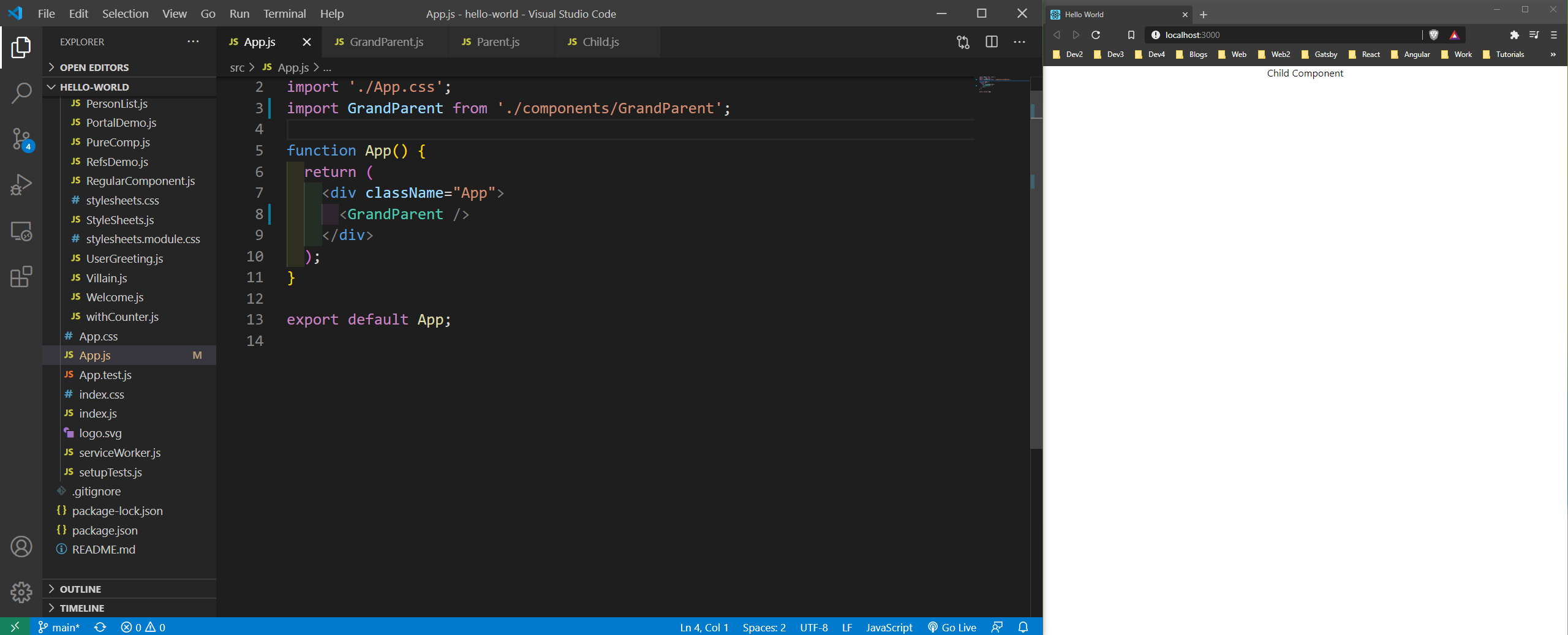 App.js
App.js
We have to first setup the context. For this create an userContext.js file inside components folder.
We create the context object with React.createContext(). It comes with a Provider and a Consumer React component. So, we will assign them to a variable and export them.
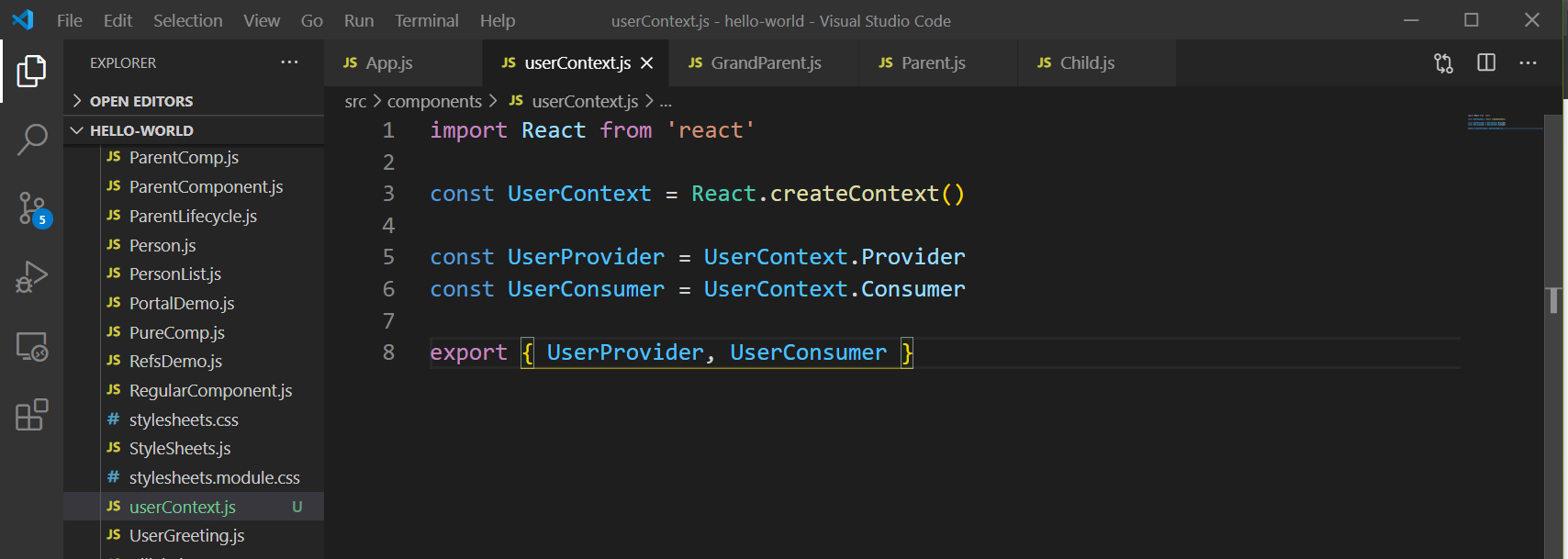 userContext.js
userContext.js
We need to use the Provider in a place, where all it’s Child component get’s it. A very good place is the App component, which is the beginning of all the Components in React.
So, in our App.js we will wrap the GrandParent component with UserProvider and pass the prop value to it. Now, it is available to all component ie GrandParent, Parent and Child.
 App.js
App.js
We want to use the username in the Child component, so we have to use UserConsumer to wrap our jsx. It contains an arrow function, where you get access to the prop from the UserProvider. Note, that we can use any name here and we are using username.
 Child.js
Child.js
There is another way to Consume the value in any component. For that we have to first export the UserContext from userContext.js file.
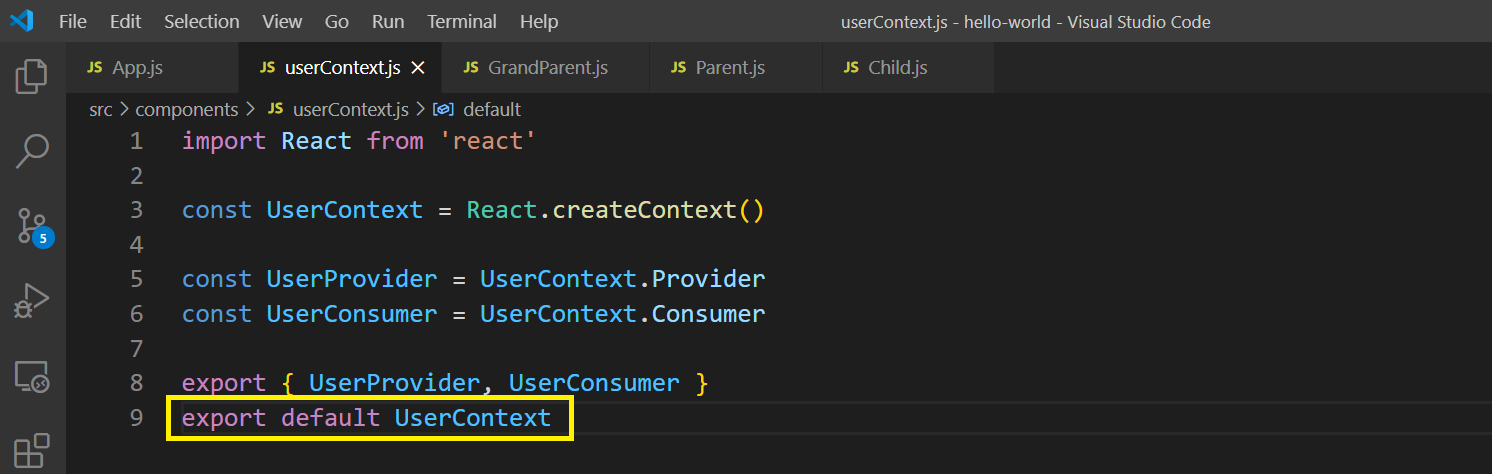 userContext.js
userContext.js
Now, we will use it in Parent component. Here, we use it with static contextType = UserContext
And it is equal simple to use it within the jsx with this.context
This way is very easy, but have a limitation that we cannot use with multiple nested Consumers.
 Parent.js
Parent.js
This completes part-17 of the series.
You can also find the code for the same in github repo, here.